What Is AI? A Practical Introduction to Artificial Intelligence and Its Evolution
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transitioned from an academic concept into a transformative force across industries—from design and healthcare to productivity tools and daily life. But what exactly is AI, where did it come from, and how has it evolved into the creative and practical tools we use today?
This foundational guide breaks down the origins, definitions, and technical underpinnings of AI, and connects them to the tools reshaping how we work, create, and solve problems.
Want to explore AI tools in action? Visit our AI Generators or Chatbot Collection to see the technology live.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
At its core, Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to computer systems that mimic human cognitive abilities—such as learning, reasoning, recognizing patterns, and solving problems. It’s not simply about performing calculations faster than a human. It’s about replicating human-like intelligence in machines in a way that can adapt and respond to varying situations.
For example:
- Midjourney specializes in visual expression, generating images based on text prompts.
- ChatGPT, on the other hand, combines language understanding, reasoning, summarization, and expression, making it one of the most comprehensive AI tools currently available.
These tools aren’t just mimicking behavior—they’re operating with a level of generalized capability that surpasses earlier generations of AI.
Where Did AI Come From? The Origins
The philosophical foundation of AI was laid by British mathematician Alan Turing, who proposed the now-famous Turing Test in 1950. His idea was simple: if a machine could engage in a conversation indistinguishable from a human, it could be said to possess “intelligence.”
In 1956, John McCarthy and others formally introduced the term “Artificial Intelligence” during a workshop at Dartmouth College. This moment marked the birth of AI as a formal academic discipline, initially dominated by rule-based systems and symbolic logic.
A well-known early achievement came when IBM’s Deep Blue defeated world chess champion Garry Kasparov—demonstrating that machines could outperform humans in highly structured, rule-based environments.
But that was just the beginning.
From Simulating to Surpassing Human Intelligence
Initially, AI aimed to simulate human decision-making—for example, automating simple tasks like arithmetic or following preset rules. Over time, researchers realized that instead of copying how humans think, AI could extend human capabilities by taking on what we struggle with:
- Processing massive datasets
- Repeating tedious tasks
- Identifying patterns invisible to the human eye
This shift—from mimicking to augmenting human intelligence—has shaped the tools we use today. Modern AI doesn’t just follow instructions; it learns, adapts, and generates.
The Five Generations of AI: Where Are We Now?
AI has gone through several phases of development:
- Rule-Based Systems: The first generation required explicit commands and had no ability to infer or adapt. Every response was hardcoded.
- Expert Systems: The second generation began integrating limited learning, but remained largely static and inflexible.
- Statistical Learning: AI began drawing inferences from datasets using basic statistical models.
- Machine Learning: The fourth generation unlocked broader learning capacity, allowing systems to improve over time.
- Deep Learning & Foundation Models: Today’s systems, such as GPT-4, rely on large datasets and neural networks to generate human-like responses and creative content with minimal instructions.
This evolution marks a shift from rules-based programming to data-driven intelligence, enabling AI tools to operate in open-ended contexts.
Narrow vs General AI: Understanding the Spectrum
Today’s AI is often categorized into two broad types:
- Narrow AI: Designed for specific tasks (e.g., facial recognition, language translation, voice assistants). Most commercial AI tools fall into this category.
- General AI: A theoretical form of AI that could perform any intellectual task a human can do. Tools like ChatGPT or Claude move us closer to this reality with their broad adaptability, but true AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) is still under development.
The rise of multi-modal tools—which process text, images, code, and more—is a step toward general intelligence, combining diverse capabilities in a single interface.
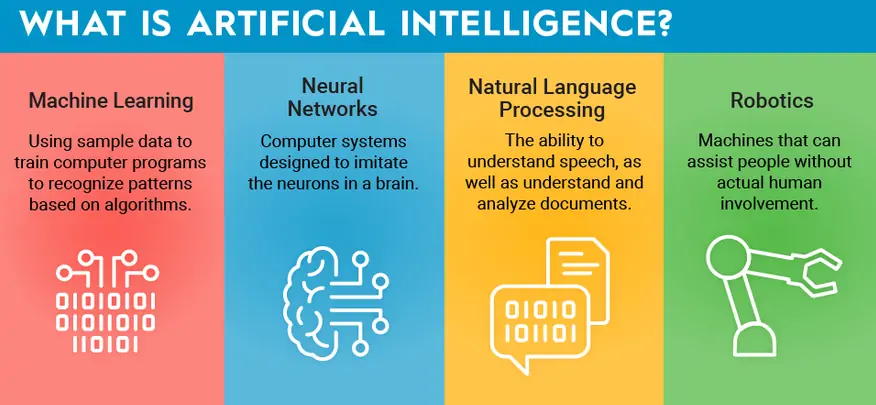
Key Technologies Powering AI Tools
Understanding the technical building blocks behind today’s tools can help users make smarter decisions when choosing AI platforms:
1. Machine Learning (ML)
ML enables systems to learn from data rather than following fixed rules.
- Supervised learning: Learns from labeled data (e.g., email spam filters).
- Unsupervised learning: Identifies hidden patterns (e.g., customer segmentation).
- Reinforcement learning: Optimizes performance via trial and error (e.g., game-playing AIs like AlphaGo).
2. Deep Learning
A subset of ML, deep learning uses multi-layered neural networks.
- CNNs (Convolutional Neural Networks): Ideal for image recognition.
- RNNs (Recurrent Neural Networks): Tailored for sequential data like speech or text.
3. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP allows machines to understand, generate, and manipulate human language.
Applications: chatbots, sentiment analysis, translation, writing assistants.
4. Computer Vision
From facial recognition to autonomous vehicles, computer vision enables machines to interpret visual data.
5. Robotics
Combining sensors, AI decision-making, and mechanical action, robotics is used in industrial automation, healthcare, and home devices.
For more detailed tool guides, explore our AI Tool Categories.
How AI Is Being Applied in the Real World
The most exciting aspect of AI isn’t just theoretical—it’s practical. Some real-world applications include:
- Consumer Tech: Personalized recommendations on platforms like TikTok or Netflix are driven by behavioral AI models.
- Healthcare: AI aids in diagnostics, medical imaging analysis, and drug discovery.
- Finance: From credit scoring to fraud detection and robo-advisors.
- Manufacturing: Smart factories use robotic process automation to boost precision and efficiency.
- Autonomous Transport: Self-driving vehicles and smart logistics systems are reshaping how we move and deliver goods.
Imagine waking up to an alarm optimized by your sleep patterns, a freshly brewed coffee made by your smart kitchen, and your schedule arranged by an AI assistant. This isn’t science fiction—it’s already happening in smart homes and productivity suites.
Explore more tools enhancing everyday life in our Productivity & Workflow section.
AI Is Not Just a Trend—It’s Infrastructure
Artificial Intelligence has evolved far beyond its early ambitions. It’s no longer just about mimicking humans—it’s about empowering us to create faster, solve harder problems, and automate what doesn’t need our attention.
Whether you're a designer exploring image-generation platforms, a developer testing code assistants, or simply curious about what comes next—AI is the new layer beneath how we live and work.
Continue your journey by exploring more tools, trends, and real-world use cases at AI-Kit.site.